 |
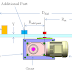
| Kinematic diagram of a cam-driven mechanism |
A simple cam-driven mechanism consist of the following parts as shown in the kinematic diagram:
- Cam: for motion generation (displacement, velocity, acceleration and timing).
- Cam follower: rolling part mounted on a lever.
- Spring (not shown): to keep contact between cam surface and cam follower.
- Lever: to transfer continuous cam rotation to swinging motion.
- Pull rod: to transfer the motion from the lever to the slider.
- Slider: end equipment (processing equipment)
In this post, we're going to focus on the pull rod (also known as push rod or tie rod) which is one of the common parts for most machines. The pull rod allows position adjustment of its connected parts since its length can be adjusted. Normally, the pull rod consists of the following parts:
- Pull rod
- Rod end bearing RH thread
- Rod end bearing LH thread
- Nut RH thread
- Nut LH thread
 |
| Pull rod with both female rod end bearings |
 |
| Example of pull rods on the machine |
The male rod end bearings version is also available. We can use the same nuts, but the hexagonal post will have threaded holes instead (see the following picture).
 |
| Pull rod with both male rod end bearings |
The increment of the pull rod length (distance between both rod end bearings) is determined by the pitch of the thread on the rod end bearings. For this example, the M10 thread has a pitch of 1.5 mm. One turn of the pull rod will change the distance of each rod end bearing by 1.5 mm. Therefore, the increment is 2 times the pitch (2 x 1.5 = 3 mm/turn).
The pull rod length is increased or decreased according to the following directions.
 |
| Pull rod length extension and retraction according to the turning direction |
The following is the animated picture showing how the slider position can be adjusted by turning the pull rod.
 |
| Animated picture of pull rod length adjustment |
Watch the following video for how the cam driven-mechanism works and where the pull rod is used in the system. The simulation uses NX4 motion simulation module.











0 comments:
Post a Comment